CDC Recommends Not Using Nasal Spray Flu Vaccine for 2016/2017 Season
Frank Magliochetti Report
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has issued its 2016-2017 influenza vaccination recommendations, which includes the use of inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) and the recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV). One of the most notable changes to the yearly recommendations is that the CDC is not recommending the use of nasal spray flu vaccinations using live attenuated 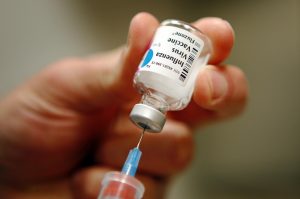 influenza vaccine (LAIV) during 2016-2017, as studies show it is not effective against preventing the flu.
influenza vaccine (LAIV) during 2016-2017, as studies show it is not effective against preventing the flu.
The studies show LAIV had no protective benefit from children ages 2 to 17. In contrast, children who received an injection were 63 percent less likely to catch influenza than are those who received no vaccination at all.
While researchers have not yet determined the underlying cause of the loss of efficacy, but it could be due to changes in the dominant viral strains circulating in the nation during flu season. LAIV worked just as well as the shot at protecting children from H3N3 and the influenza B strain in recent flu seasons, according to a study published in the journal Pediatrics, but youngsters who received LAIV were three times more likely to suffer infection with H1N1 than were children who got the shot.
H1N1 has been the dominant strain for the past few years, according to a February 2016 CDC report, which means LAIVs can leave patients unprotected from the strains most likely to cause illness this flu season.
About Vaccinations, LAIVs, and Flu Season
Influenza vaccinations protect millions of people in the United States from developing influenza each year. Flu shots also reduce severity of influenza symptoms when it does develop, and prevents  hospitalizations relating to the flu. CDC recommends yearly flu shots for everyone 6 months and older. Antibodies typically take about two weeks to develop.
hospitalizations relating to the flu. CDC recommends yearly flu shots for everyone 6 months and older. Antibodies typically take about two weeks to develop.
Many patients, and parents of pediatric patients, prefer LAIVs because of the perceived pain or trauma of an injection. LAIVs have been under development in the United States since the 1960s, according to the CDC, and the intranasal, trivalent, cold-adapted, live, LAIV received approval in 2003 as an option for among health patients aged 5 to 49 years. Because the nasal spray contains live, weakened influenza viruses, LAIV theoretically stimulates a stronger immune response than the shots, which contain killed viruses.
Influenza activity often begins to increase in October and peak sometime in late winter or early spring. The peak week of flu activity for the 2015-2016 season occurred on the last week of March 2016,
according to the CDC, which was one of the later season peaks on record. The CDC’s adjusted overall vaccine effectiveness (VE) against influenza A and B viruses for all ages was 47 percent, while the overall VE against A(H1N1)pdm09 was 41 percent and the overall VE against influenza B was 55 percent.
Vaccine manufacturers will provide an estimated 157 to 168 million doses of injectable influenza vaccine for the U.S. market. This is on par with last year’s vaccine distribution.
Source
https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/65/rr/rr6505a1.htm?s_cid=rr6505a1_w
https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/han00387.asp
https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr5213a1.htm
http://www.cdc.gov/flu/about/season/flu-season-2015-2016.htm
https://www.cdc.gov/flu/professionals/vaccination/vaccinesupply.htm
Frank Magliochetti is Managing Partner for Parcae Capital.
-
North Andover, Massachusetts
This column of posts is directed at the Healthcare Industry. Frank plans to release a new site dedicated to the industry. He currently assists companies who are building, restructuring, transforming and resurrecting there business’s. An example of his client base are, Xenetic Biosciences , IPC Medical Corp, Just Fellowship Corp, Environmental Services Inc., Parsons Post House LLC, ClickStream Corporation as well as having a business talk radio show; The Business Architect on the URBN network.